Login Queue
The Login Queue feature is only available for AccelByte Gaming Services (AGS) Private Cloud users.
Overview
The AGS Login Queue feature provides an elegant solution to manage the influx of players during times of high traffic. These events can include game launches, major updates, or peak hours. This feature prevents server overloads and ensures a smoother experience for players by gradually allowing them to access the game instead of overwhelming the server all at once.
In the gaming industry, this feature is also commonly referred to as "waiting room."
The Login Queue feature allows you to provide players their current position and estimated wait time in the queue. This provides a more organized and predictable experience.
Here is an example of a login queue in a popular game:

Configure Login Queue
In this section, you will learn how to configure the Login Queue and how it works.
Basic configuration
The Login Queue can be activated per game namespace by setting up the feature configuration. Setting up the Login Queue is straightforward. There are only two essential properties which need to be handled by game developers:
Max concurrency: The maximum number of players who can be logged in at the same time (e.g., 1,000,000 players).
Max Login rate per second: The maximum number of player logins that can be handled by the account system per second (e.g., 500 logins per second).
Advanced configuration
After setting the two required properties, admins can activate the login queue for a game directly by clicking the Activate button in the configuration.
If you have specific requirements and want more in-depth customization of the login queue, AGS provides a couple of advanced property settings. In general, these will be set with default values, but you can modify them as needed.
Safety Margin: Margin triggering the queue before reaching the max concurrency. For example, if the max concurrency is set to 1,000,000, a value of 5% means the queue starts when concurrency reaches 950,000 players.
Cool-Down: When the login queue is enabled, the game will wait for this amount of time pass without a trigger before deactivating the queue. For example, 300 seconds. This is because we want to prevent the Login Queue being enabled or disabled too frequently. It is also increases Login Queue performance and reduces unnecessary resource cost.
Queue Reconnect Grace Duration: Duration for the players to reconnect before losing their position in the queue. If a player reconnects during the grace period, they will be inserted at their last known position. For example, if they were at position 500 and they reconnect, they will go back to position 500.
Player Reconnect Grace Duration: Duration for logged in players to reconnect to the game before being put in the queue when they disconnect or sign off. If they were fully logged in, they go back to the queue at position zero (i.e., the top of the queue).
Polling Time: Maximum duration for the game client to refresh the queue info for a player.
Exemption configuration
There are also cases where you'd want to skip the login queue or insert specific user accounts at the top of the queue. The following configuration options are designed for these scenarios.
Exempted Accounts: Multiple specific accounts that should be excluded from the login queue. For example, administration accounts, QA accounts, or VIP accounts.
Exempted IAM Clients: Specific applications that should be excluded from the login queue. For example, you've created a web portal for the game and you don't want to put players into the queue when they sign into that website, but you want to do so for the game client.
Sample use cases
When a large number of players attempt to log in simultaneously, it can put a significant strain on the game servers. The AGS Login Queue helps manage the influx, preventing server crashes or instability that could negatively impact the gaming experience for everyone. Here are some sample use cases:
Game launch:
Scenario: A highly anticipated game is launching, and thousands of players are eager to log in and start playing.
Use Case: You implement a login queue to prevent server overload, ensuring a smooth launch and allowing players to enter the game gradually.
Major update release:
Scenario: A game releases a significant update with new features, content, or fixes. This attracts a surge of players wanting to experience the changes.
Use Case: To avoid server instability and provide fair entry for all players, you can activate a login queue during the initial hours of the update.
Special events or promotions:
Scenario: Your game hosts a special in-game event or promotion that attracts a large player turnout.
Use Case: You use a login queue to help manage the increased player activity, preventing server crashes and ensuring that everyone has a fair chance to participate in the event.
Free-to-play weekends:
Scenario: Your game offers a free-to-play weekend, resulting in a sudden influx of players trying out the game.
Use Case: To accommodate the temporary increase in player numbers, you implement a login queue to avoid overwhelming the servers and maintain a stable gaming experience.
Server maintenance:
Scenario: Scheduled server maintenance or updates are underway and players are attempting to log back in once the maintenance is completed.
Use Case: You employ a login queue to manage the initial rush of players returning to the game after maintenance. This prevents server instability.
Peak hours:
Scenario: There are certain peak hours during the day when a large number of players log in simultaneously.
Use Case: To distribute the incoming player load evenly and prevent server strain during peak times, you use a login queue to regulate access.
Interaction
This section explains how you can use various Login Queue features.
Add players to queue
The login queue is the first login step of user authentication to a game namespace. It happens right after the authentication but before anything else such as checking legal documents.
While the player is in the queue, they have a minimum set of permissions Basically, the only one action the queued players can perform is to logout or cancel the queue. This aborts the login process and frees their spot in the queue.
Queued players can be aware of their position in the queue and estimated wait time until they are out of the queue. This is handled by AGS automatically.
Enable Login Queue
Once you have set up the login queue configuration, you can enable the login queue by multiple automatic triggers:
- Automatic Trigger 1: When the concurrency reaches the configured Max concurrency minus the Safety Margin, the login queue is enabled.
- Automatic Trigger 2: When the Max Login rate per second is reached, the login queue is enabled.
Disable Login Queue
The login queue will be disabled when both of these criteria are met:
- Criterion 1: None of the automatic enabling triggers are met during the Cooldown.
- Criterion 2: The queue reaches zero.
Display current position and estimated wait time
When the queue is enabled, the players have to wait for the concurrency to drop below the maximum concurrency to be processed. The queue is processing logins at the maximum rate equal to Login rate.
Integration with AGS SDK
- Unreal Engine
- Unity Engine
Integration with Unreal OSS
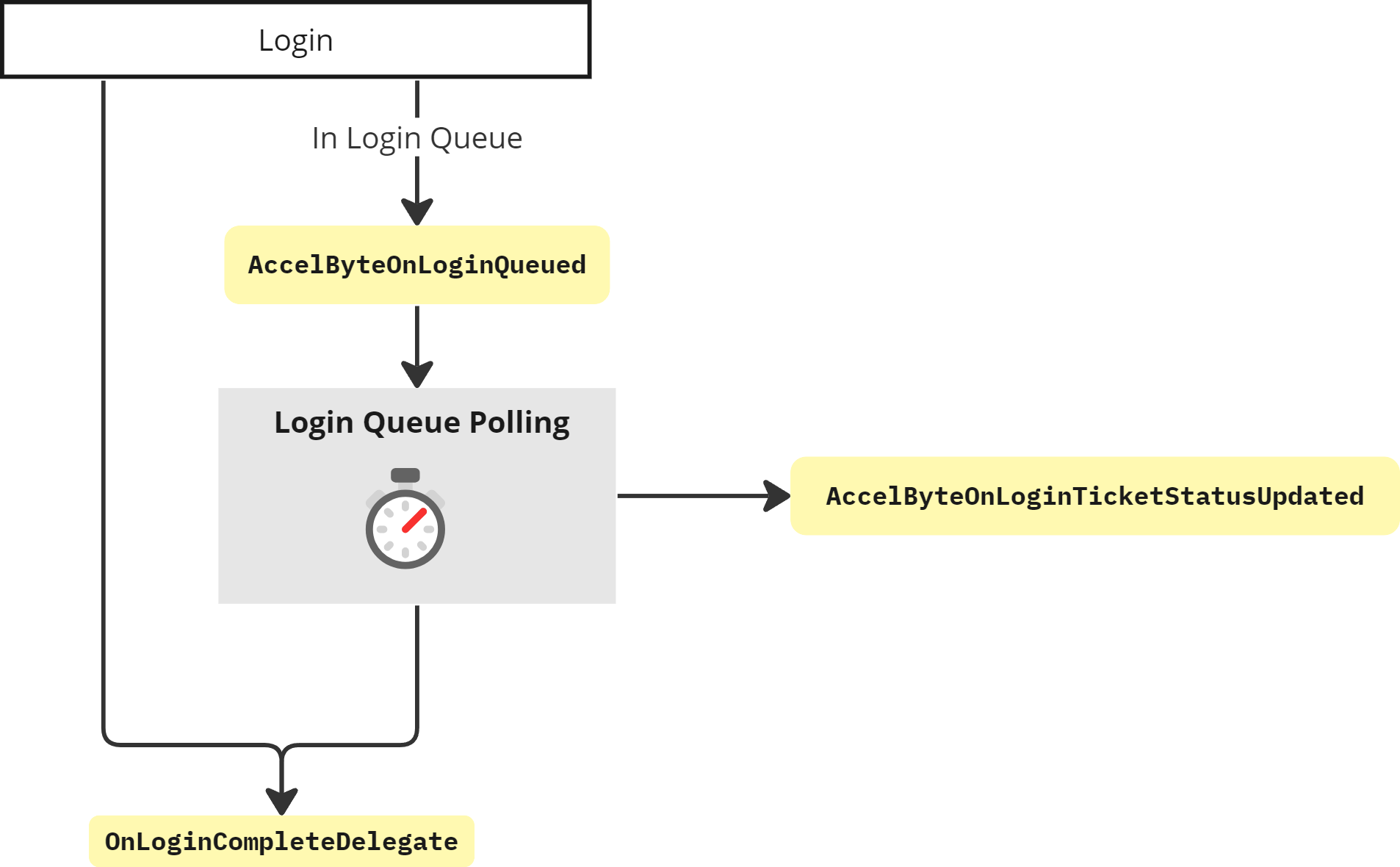
Login Queue is seamlessly built into the Login APIs in the AccelByte OSS. When Login Queue features are enabled, the AccelByte OSS handles all queuing, progression and provides updates for your game title to listen to and update the UI accordingly. When the head of the queue is reached, login can be completed and the OnLoginCompleteDelegate is triggered.
When Login Queue features are not enabled, Login functions as normal and the OnLoginCompleteDelegate is triggered immediately.
Config
The Login Queue behavior can be adjusted via the DefaultEngine.ini file, under the [OnlineSubsystemAccelByte] section.
LoginQueuePresentationThreshold
Login Queue wait times can be very short. To prevent instances of the in-game UI being triggered for an abruptly short period of time, you can use this threshold to only trigger the AccelByteOnLoginQueued delegate if the estimated wait time warrants it.
When the expected wait time is short but acceptable (i.e., below this threshold), your game title can treat this as a conventional login flow.
Example:
[OnlineSubsystemAccelByte]
bEnabled=true
; trigger OnLoginQueued delegate if estimated wait time is longer than five seconds
LoginQueuePresentationThreshold=5
Unreal Login API
The following is how to integrate Login APIs using AccelByte OSS.
void AClassPlayerController::BeginPlay()
{
...
auto ABSubsystem = IOnlineSubsystem::Get(ACCELBYTE_SUBSYSTEM);
auto IdentityInterface = ABSubsystem->GetIdentityInterface();
int32 LocalUserNum = 0;
// Auto-detect the login methods based on the configuration
FOnlineAccountCredentialsAccelByte Credentials{};
// Login
IdentityInterface->AddOnLoginCompleteDelegate_Handle(LocalUserNum
, FOnLoginCompleteDelegate::CreateLambda(
[](int32 LocalUserNum, bool bLoginWasSuccessful, const FUniqueNetId& UserId, const FString& LoginError)
{
if (bLoginWasSuccessful)
{
// Do something when player successfully logs in
}
else
{
// Do something when player failed to log in
}
}));
IdentityInterface->Login(LocalUserNum, Credentials);
}
Login Queue API Delegates
AccelByteOnLoginQueued
On Login, if the Login Queue is enabled and capacity has been reached, the player will enter the Login Queue and the AccelByteOnLoginQueued delegate will be triggered.
The delegate will return TicketInfo containing:
- Ticket ID
- Position in the queue
- Estimated waiting time
- Reconnect expiration time
void AClassPlayerController::OnLoginQueued(int32 LocalUserNum, const FAccelByteModelsLoginQueueTicketInfo& TicketInfo)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Login request for LocalUserNum %d is queued with Ticket Id: %s - Position: %d - EstimatedWaitingTime: %d - Expire Time: %d"), LocalUserNum, *TicketInfo.Ticket, TicketInfo.Position, TicketInfo.EstimatedWaitingTimeInSeconds, ReconnectExpiredAt);
// Do something when queued
}
void AClassPlayerController::BeginPlay()
{
...
auto ABSubsystem = IOnlineSubsystem::Get(ACCELBYTE_SUBSYSTEM);
auto IdentityInterface = ABSubsystem->GetIdentityInterface();
int32 LocalUserNum = 0;
IdentityInterface->AddAccelByteOnLoginQueued_Handle(LocalUserNum
, FAccelByteOnLoginQueuedDelegate::CreateRaw(this, &AClassPlayerController::OnLoginQueued));
}
The AccelByteOnLoginQueued will only be triggered if the estimated waiting time is greater than the LoginQueuePresentationThreshold set in the config.
AccelByteOnLoginTicketStatusUpdated
Within the AccelByte OSS, there is a polling mechanism to periodically refresh the queue position and provide updates for the game title to listen to and update UI accordingly.
With each poll, an AccelByteOnLoginTicketStatusUpdated is triggered.
For successful polls, the delegate will return TicketInfo containing:
- Ticket ID
- Position in the queue
- Estimated waiting time
- Reconnect expiration time
In the unlikely event that an error occurs, details will be contained in the error message.
void AClassPlayerController::OnLoginTicketStatusUpdated(int32 LocalUserNum, bool bWasSuccessful, const FAccelByteModelsLoginQueueTicketInfo& TicketInfo, const FOnlineErrorAccelByte& Error)
{
if (bWasSuccessful)
{
// Do something when successful
}
else
{
// Do something when failed
}
}
void AClassPlayerController::BeginPlay()
{
...
auto ABSubsystem = IOnlineSubsystem::Get(ACCELBYTE_SUBSYSTEM);
auto IdentityInterface = ABSubsystem->GetIdentityInterface();
int32 LocalUserNum = 0;
IdentityInterface->AddAccelByteOnLoginTicketStatusUpdated_Handle(LocalUserNum
, FAccelByteOnLoginTicketStatusUpdatedDelegate::CreateRaw(this, &AClassPlayerController::OnLoginTicketStatusUpdated));
}
Cancel Unreal Login Queue API
The Login Queue process can be canceled at any time.
void AClassPlayerController::BeginPlay()
{
...
auto ABSubsystem = IOnlineSubsystem::Get(ACCELBYTE_SUBSYSTEM);
auto IdentityInterface = ABSubsystem->GetIdentityInterface();
int32 LocalUserNum = 0;
IdentityInterface->CancelLoginQueue(LocalUserNum);
}
Cancel Login Queue API Delegates
AccelByteOnLoginQueueCancelComplete
When the CancelLoginQueue process completes, the AccelByteOnLoginQueueCancelComplete delegate will be triggered.
void AClassPlayerController::OnLoginQueueCancelCompleted(int32 LocalUserNum, bool bWasSuccessful , const FOnlineErrorAccelByte& Error)
{
if (bWasSuccessful)
{
// Do something when successful
}
else ..
{
// Do something when failed
}
}
void AClassPlayerController::BeginPlay()
{
...
auto ABSubsystem = IOnlineSubsystem::Get(ACCELBYTE_SUBSYSTEM);
auto IdentityInterface = ABSubsystem->GetIdentityInterface();
int32 LocalUserNum = 0;
IdentityInterface->AddAccelByteOnLoginQueueCancelComplete_Handle(LocalUserNum
, FAccelByteOnLoginQueueCancelCompleteDelegate::CreateRaw(this, &AClassPlayerController::OnLoginQueueCancelCompleted));
}
Integration with Unity
Login Queue is seamlessly built into the Login APIs. When Login Queue features are enabled, the AGS Unity SDK handles all queuing, progression and provides updates for your game title to listen to and update the UI accordingly. When the head of the queue is reached, login can be completed and the LoginCallback is triggered.
Prerequisites
Include the following references to use Login Queue.
using AccelByte.Api;
using AccelByte.Core;
using AccelByte.Models;
Use the function below to get the API client to interact with AGS.
var userWrapper = AccelByteSDK.GetClientRegistry().GetApi().GetUser();
Setup Login Queue
To get the update event, get the cancellation event and do the cancellation in the login queue API. Each login queue API's optional parameter always has these parameters:
- CancellationToken: Token that can be used to cancel the polling mechanism.
- LoginTimeout: Set the login timeout in milliseconds to avoid an error or getting stuck in the polling mechanism when the login queue is running. By default, this value is 120 seconds and can't be set below 30 seconds.
- OnQueueUpdateEvent: A polling mechanism to periodically refresh the queue position and provide updates for the game title to listen to and update the UI accordingly. With each successful poll, it will trigger this event. This event will return a
LoginQueueTicketthat contains:- Ticket ID
- Position in the queue
- Estimated waiting time
- Reconnect expiration time
- OnCancelledEvent: This event will be triggered when the queue mechanism is being cancelled.
If you don't want to add the cancellation and get an update event from the API, you can leave the optional parameter empty or use an override function that doesn't have an optional parameter in the parameter .
Unity Login API
This example shows how to integrate the Login Queue APIs using the AGS Unity SDK.
string ticket;
CancellationTokenSource loginCts = new CancellationTokenSource();
// Set the optional parameter for login with email
// Each login method has each own optional parameter
LoginWithEmailV4OptionalParameters optionalParameters = new LoginWithEmailV4OptionalParameters()
{
OnQueueUpdatedEvent = queueTicketResult =>
{
// Do something when there is an update from the refresh queue ticket
ticket = queueTicketResult.Ticket ?? ticket;
},
OnCancelledEvent = () =>
{
// Do something when ticket is cancelled
},
// Set the login timeout into 60000 milliseconds or 60 seconds
LoginTimeout = new LoginV4Timeout(60 * 1000),
// Set the cancellation token that can be used to cancel the login queue process
CancellationToken = loginCts.Token
};
// Call login method that use Login Queue API
userWrapper.LoginWithEmailV4(Email
, Password
, optionalParameters
, result =>
{
if (result.IsError)
{
// Do something if the operation fails
Debug.Log("Login failed");
return;
}
// Do something if the operation succeeds
Debug.Log("Login successful");
});
There are some other login Queue APIs supported for login queue. Here are all of the Login Queue APIs:
Login with Email
LoginWithEmailV4(string email, string password, ResultCallback<TokenData, OAuthError> loginCallback);
LoginWithEmailV4(string email, string password, LoginWithEmailV4OptionalParameters optionalParams, ResultCallback<TokenData, OAuthError> loginCallback);
Login with Device Id
LoginWithDeviceIdV4(ResultCallback<TokenData, OAuthError> loginCallback);
LoginWithDeviceIdV4(LoginV4OptionalParameters optionalParams, ResultCallback<TokenData, OAuthError> loginCallback);
Login with Other Platform
LoginWithOtherPlatformV4(PlatformType platformType, string platformToken, ResultCallback<TokenData, OAuthError> loginCallback);
LoginWithOtherPlatformV4(PlatformType platformType, string platformToken, LoginWithOtherPlatformOptionalParameters optionalParams, ResultCallback<TokenData, OAuthError> loginCallback);
Login with Other Platform Id
LoginWithOtherPlatformIdV4(string platformId, string platformToken, ResultCallback<TokenData, OAuthError> loginCallback);
LoginWithOtherPlatformIdV4(string platformId, string platformToken, LoginWithOtherPlatformOptionalParameters optionalParams, ResultCallback<TokenData, OAuthError> loginCallback);
Login with Refresh Token
LoginWithRefreshTokenV4(string refreshToken, ResultCallback<TokenData, OAuthError> loginCallback);
LoginWithRefreshTokenV4(string refreshToken, LoginV4OptionalParameters optionalParams, ResultCallback<TokenData, OAuthError> loginCallback);
Generate Game Token
GenerateGameTokenV4(string code, ResultCallback<TokenData, OAuthError> loginCallback);
GenerateGameTokenV4(string code, LoginV4OptionalParameters optionalParams, ResultCallback<TokenData, OAuthError> loginCallback);
Create Headless Account and Response Token
CreateHeadlessAccountAndResponseTokenV4(string linkingToken, bool extendExp, ResultCallback<TokenData, OAuthError> loginCallback);
CreateHeadlessAccountAndResponseTokenV4(string linkingToken, bool extendExp, LoginV4OptionalParameters optionalParams, ResultCallback<TokenData, OAuthError> loginCallback);
Authentication with Platform Link and Login
AuthenticationWithPlatformLinkAndLoginV4(string email, string password, string linkingToken, ResultCallback<TokenData, OAuthError> loginCallback);
AuthenticationWithPlatformLinkAndLoginV4(string email, string password, string linkingToken, LoginV4OptionalParameters optionalParams, ResultCallback<TokenData, OAuthError> loginCallback);
Verify 2 FA Code
Verify2FACodeV4(string mfaToken, TwoFAFactorType factor, string code, ResultCallback<TokenData, OAuthError> loginCallback);
Verify2FACodeV4(string mfaToken, TwoFAFactorType factor, string code, Verify2FACodeV4OptionalParameters optionalParams, ResultCallback<TokenData, OAuthError> loginCallback);
Cancel Unity Login Queue API
To support cancellation of the Unity Login Queue mechanism, you must provide both a CancellationToken and an OnCancelledEvent callback as part of the optional parameters. These are configured during the setup process, as outlined in Setup Login Queue.
Below is an example demonstrating how to configure and use these optional parameters to cancel a login request.
// Create a CancellationTokenSource to control cancellation
CancellationTokenSource loginCts = new CancellationTokenSource();
// Set the optional parameter for login with email
LoginWithEmailV4OptionalParameters optionalParameters = new LoginWithEmailV4OptionalParameters()
{
OnCancelledEvent = () =>
{
// Handle the cancellation event
Debug.Log("Login cancelled");
},
CancellationToken = loginCts.Token
};
// Initiate the login request using the Login Queue API
userWrapper.LoginWithEmailV4(Email
, Password
, optionalParameters
, result =>
{
if (result.IsError)
{
// Do something if the operation fails
Debug.Log("Login failed");
return;
}
// Do something if the operation succeeds
Debug.Log("Login successful");
});
To cancel an ongoing login attempt, simply invoke the Cancel() method on the previously created CancellationTokenSource. This will trigger the cancellation token and execute the OnCancelledEvent callback.
// Trigger login cancellation
loginCts.Cancel();
FAQ
Q: Is Login Queue available in the Publisher namespace?
A: No, Login Queue is only available in Game Namespaces.
Q: Will AGS provide players with the Total Queue Size, the current queue position, and the estimated wait time at the game client side?
A: No, AGS will only return and display the player's current queue position and estimated wait time on the game client side.
Q: Does the Login Queue gate the create user endpoint for new user creation?
A: No, Login Queue only gates user logins in game namespaces.